According To Dalemberts Principle
According To Dalemberts Principle. D'Alembert's principle, also known as the Lagrange-d'Alembert principle, is a statement of the fundamental classical laws of motion. The virtual shifts or rotations are obtained from the partial derivatives of the translational or rotational position coordinates according to the generalized.
It is named after its discoverer, the French physicist and mathematician Jean le Rond d'Alembert.
D-ALEMBERT'S PRINCIPLE What is D-Alembert's Principle in Engineering Mechanics?
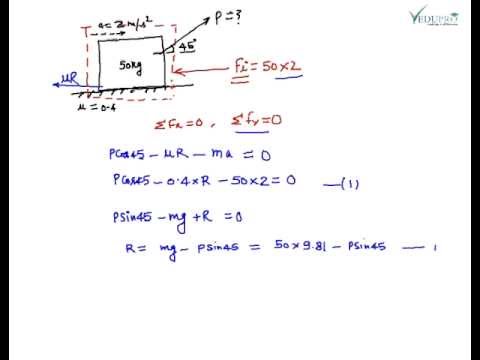
One of the fundamental principles of mechanical systems with constraints; it involves a general method with the aid of which the equations of motion of any mechanical system may be derived in the form of equilibrium equations of forces (in this sense d'Alembert's principle "reduces" dynamics to statics). Double Pendulum: Find the EOM of the. double pendulum shown at the right using. According to the d'Alembert's principle, the external forces acting on a body and the resultant inertia forces on a body are in.







0 Response to "According To Dalemberts Principle"
Posting Komentar